Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body fails to properly regulate blood sugar levels, leading to elevated glucose levels. Diabetes can have serious health implications if not managed effectively. In this article, we will delve into the risk factors associated with diabetes, the importance of early detection, the role of lifestyle changes, and the latest advancements in medical research related to its prevention.
Risk Factors for Diabetes

Diabetes is a complex metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels. There are several risk factors associated with the development of diabetes, including:
1. Obesity
Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can impair insulin action and contribute to insulin resistance.
2. Family History
Having a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, with diabetes increases your risk. There is a genetic component to diabetes, although lifestyle factors also play a role.
3. Physical Inactivity
Lack of regular physical activity can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of diabetes. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
4. Unhealthy Diet
A diet high in processed foods, sugary beverages, saturated and trans fats, and low in fiber is associated with an increased risk of diabetes. Consuming excessive amounts of sugary and refined carbohydrates can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
5. Age
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with age. This may be due to factors such as reduced physical activity, muscle mass decline, and overall decreased metabolic efficiency.
6. High Blood Pressure
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is often associated with diabetes. The combination of the two conditions increases the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Smoking
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. It can contribute to insulin resistance and other metabolic abnormalities.
Diabetes is influenced by various factors. Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, and unhealthy eating habits are prominent risk factors. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps towards prevention.
Early Detection of Diabetes
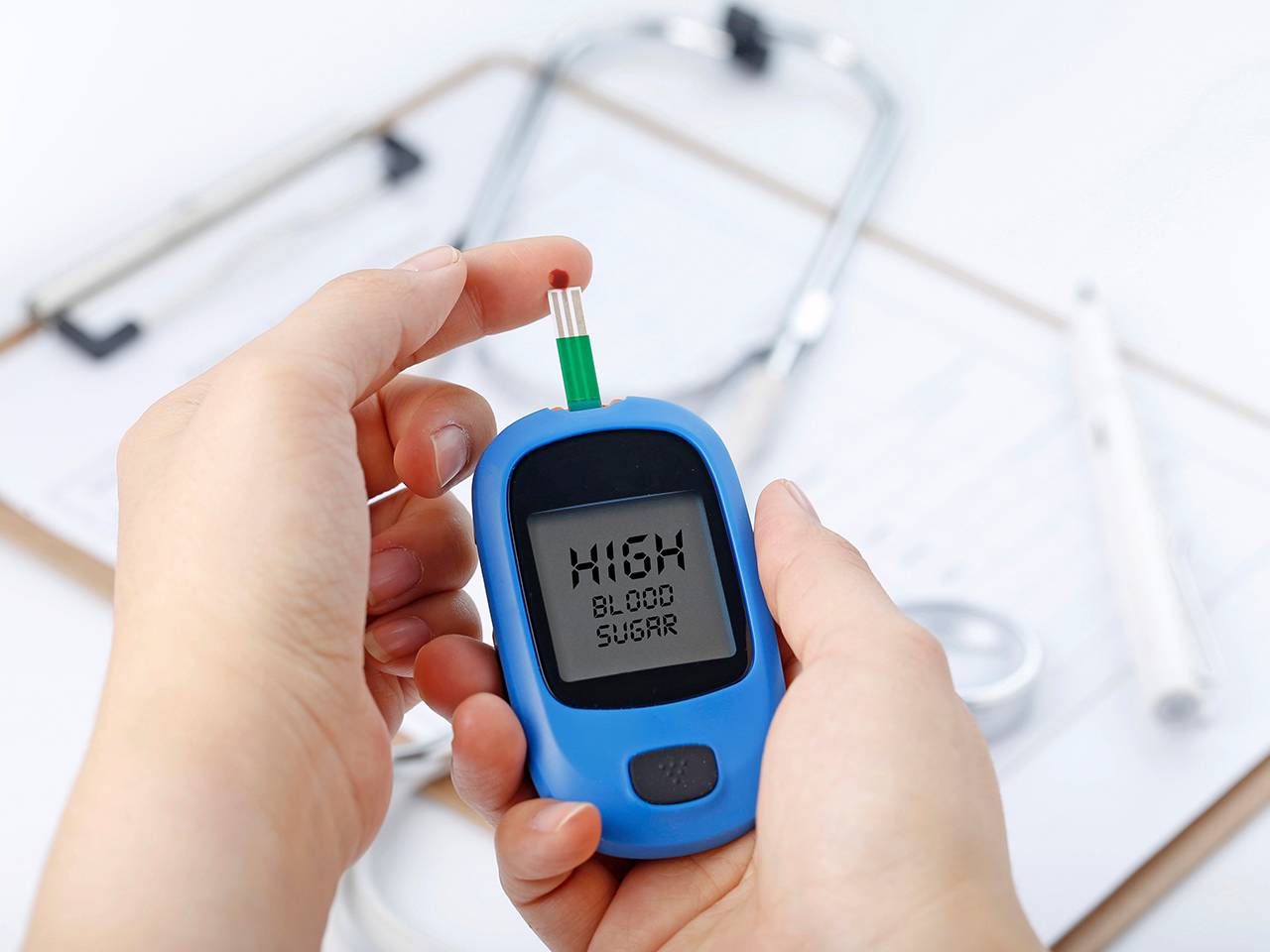
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for effective management and to prevent complications. Here are some methods and tests used for early detection:
1. Symptom Awareness
Be aware of common symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and frequent infections. If you experience these symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare professional.
2. Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test
This blood test measures your blood glucose level after fasting for at least 8 hours. A fasting plasma glucose level of 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or higher on two separate occasions is indicative of diabetes.
3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
This test measures your blood glucose levels before and 2 hours after consuming a glucose-rich beverage. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher after 2 hours indicates diabetes.
4. Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Test
This blood test measures the average blood glucose level over the past 2-3 months. An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher is indicative of diabetes.
5. Random Plasma Glucose Test
This test measures your blood glucose level at any time of the day, regardless of when you last ate. If the level is 200 mg/dL or higher, along with diabetes symptoms, it suggests diabetes.
6. Risk Assessment Tools
Some healthcare providers use risk assessment tools, such as questionnaires or calculators, to estimate an individual's risk of developing diabetes. These tools consider factors like age, family history, body weight, physical activity, and blood pressure.
7. Routine Check-ups
Regular health check-ups with a healthcare professional can help identify early signs of diabetes. They may assess your medical history, conduct physical examinations, and order blood tests to monitor blood glucose levels.
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. Regular blood tests that measure blood sugar levels, such as fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c tests, can detect diabetes or prediabetes. It is recommended that individuals with risk factors or those above the age of 45 undergo regular screenings to ensure timely intervention.
Lifestyle Changes

Lifestyle modifications are key in the management of diabetes, particularly for type 2 diabetes. They play a vital role in controlling blood sugar levels, preventing complications, and improving overall health. Here are some important lifestyle changes that can help manage diabetes:
1. Healthy Eating
Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is essential. Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit the intake of sugary and processed foods, as well as foods high in saturated and trans fats. Monitoring portion sizes and practicing mindful eating can also be beneficial.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, and promotes weight management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, spread throughout the week. Additionally, incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass.
3. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight or working towards weight loss (if overweight) is important for managing diabetes. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. A combination of a balanced diet and regular physical activity is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
4. Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for understanding how different foods, physical activity, and medications affect your diabetes management. This information can help you make necessary adjustments to your diet, exercise routine, and medication, under the guidance of your healthcare provider.
5. Medication Management
If prescribed medication for diabetes management, it's important to take it as prescribed and follow your healthcare provider's instructions. Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan can help keep blood sugar levels within the target range and prevent complications.
6. Stress Management
Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels and overall well-being. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as through relaxation techniques, exercise, hobbies, or counseling, can positively impact diabetes management.
7. Quit Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of various complications related to diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, and circulation problems. Quitting smoking is highly beneficial for overall health and diabetes management.
8. Regular Check-ups and Self-Care
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your diabetes management, adjust medications if needed, and address any concerns. Additionally, practice good self-care by maintaining good hygiene, taking care of your feet, and managing any other health conditions you may have.
Lifestyle modifications play a vital role in managing diabetes. A healthy diet comprising balanced portions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential. It is advisable to choose complex carbohydrates over refined ones, such as whole grains instead of white bread or pasta. Regular physical activity helps control weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and lowers blood sugar levels. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption also contribute to better diabetes management.
Advancements in Medical Research
Medical research continually strives to enhance diabetes prevention strategies. Here are some ways medical research contributes to diabetes prevention:
1. Development of Screening Tools
Medical research contributes to the development of screening tools and risk assessment models that can help identify individuals at high risk of developing diabetes. These tools enable healthcare providers to identify individuals who may benefit from early intervention and preventive measures.
2. Medication Trials
Researchers conduct clinical trials to evaluate the effectiveness of various medications in preventing or delaying the onset of diabetes. For example, studies have explored the use of certain diabetes medications, such as metformin, in individuals at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These trials provide evidence-based guidelines for the use of medications in diabetes prevention.
3. Behavioral Interventions
Research explores behavioral interventions, such as education programs, counseling, and support groups, to promote healthy lifestyle changes and adherence to preventive measures. Understanding the most effective behavioral strategies helps tailor interventions for different populations and improve long-term adherence.
4. Targeted Approaches
Medical research aims to identify subgroups of the population that may be at higher risk of developing diabetes or have unique risk factors. This knowledge allows for targeted prevention strategies to be developed, considering factors such as age, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and comorbidities.
5. Healthcare System Improvements
Research contributes to improving healthcare systems' infrastructure and policies to support diabetes prevention. This includes implementing preventive measures in primary care, developing effective healthcare delivery models, and integrating prevention efforts into routine healthcare practices.
6. Public Health Initiatives
Research findings guide public health initiatives and policies aimed at diabetes prevention. This can include awareness campaigns, community-based interventions, and policy changes to promote healthy environments and lifestyles.
Medical research continually strives to enhance diabetes prevention strategies. Recent advancements include the development of artificial pancreas systems, which automate insulin delivery based on blood sugar levels. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential benefits of gene therapy and stem cell transplantation in treating diabetes. These advancements provide hope for more effective prevention and treatment methods in the future.
Conclusion

Diabetes is a prevalent and serious health condition that requires attention and proactive management. By understanding the risk factors, detecting diabetes early, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed about the latest medical research, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risks associated with diabetes. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals and following their guidance are crucial for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels and leading a healthy life. With ongoing advancements in medical research, there is hope for improved prevention and treatment methods to combat diabetes effectively. Together, we can strive towards a future where diabetes is better understood, managed, and prevented, leading to healthier lives for individuals worldwide.
Check out Hello Fitness Magazine. There is never a wrong time to go on a fitness quest. Contact us and allow us to assist you in leading a better lifestyle. Follow us on Instagram. We share the best Health & Fitness related Articles for information based on healthy eating, health and fitness recommendations, health problems and their solutions, human body fitness, and much more.