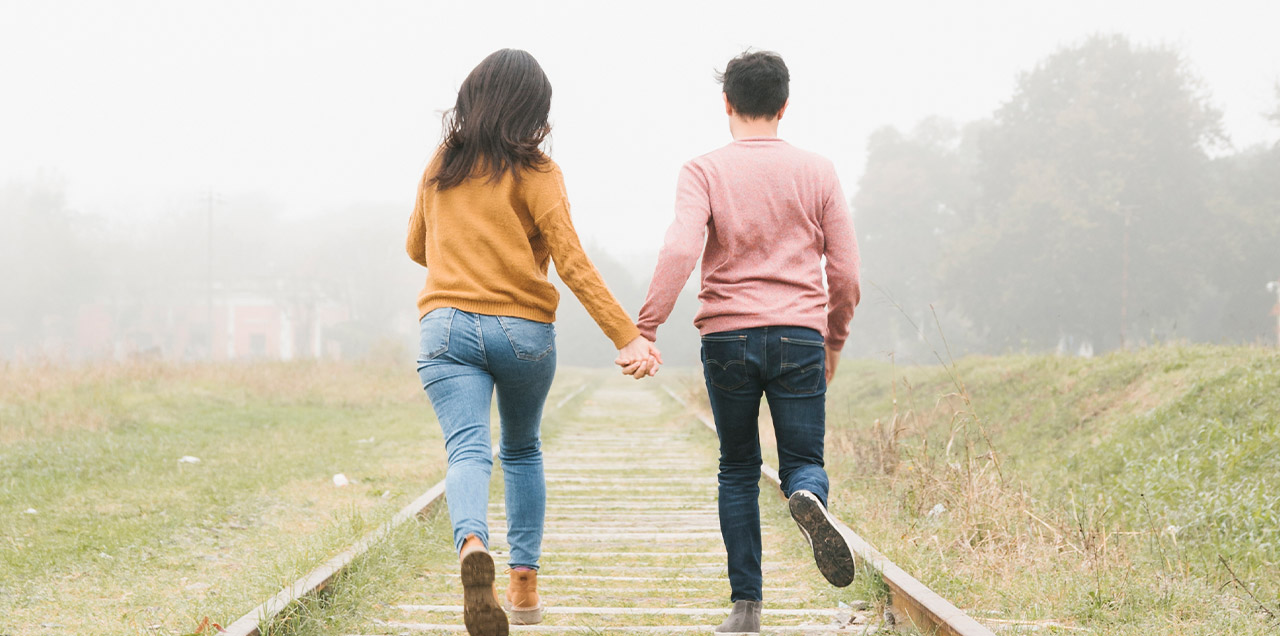
There are roughly 6 types of relationships a human shares with another in a lifespan. Amongst them, romantic relationships are known to be the most significant. I am stating this because society has evolved in a certain way to believe this. They say, the continuity of the circle of life or the society’s loop depends upon this particular romantic relationship, which is shared between a man and a woman. The cavemen evolved to build a civilized society where they developed kinships. This society likes to follow systems in everything, they built social systems, economic systems, political systems, and kin systems. But one loophole that affects this whole hierarchal, capitalist, sophisticated arrangement, is ‘emotions’, which we can say are so consistent with its inconsistent nature since eternity. These emotion affects romantic kinships a lot making them the most complex arrangement.
As a result, romantic relationships have undergone a remarkable transformation over the centuries, reflecting broader social, economic, and cultural shifts. From the rigid conventions of ancient times to the fluid and diverse forms of partnerships seen today, the evolution of kinship between men and women is a fascinating journey through history.
Let's know it from the beginning
Ancient and Medieval Times: Duty Over Desire
In ancient civilizations, romantic relationships were often dictated by societal needs and familial duties rather than personal choice or emotional connection. Marriages were typically arranged to consolidate wealth, secure alliances, or continue family lineage. Love and personal happiness were secondary considerations.
For instance, in Ancient Rome, Europe, and India, marriages were strategic decisions made by the head of the household, and the concept of romantic love as a basis for marriage was almost non-existent. Similarly, in medieval Europe, noble marriages were arranged to forge political alliances and ensure the continuation of noble bloodlines.
The Renaissance and Enlightenment: Emergence of Romantic Ideals
The Renaissance and Enlightenment periods marked a shift towards individualism and personal freedom, gradually altering perceptions of romantic relationships. Literature and art began to celebrate the idea of romantic love. The works of Shakespeare, for example, often explored themes of love and passion, reflecting a growing societal interest in romantic partnerships. During this time, the concept of courtly love emerged, particularly in Europe. This was an idealized and often extramarital form of love that emphasized chivalry and admiration, reflecting a more emotional and individualized approach to relationships, albeit within a structured and often constrained framework.
While Europe marked a shift towards individualism and personal freedom, India experienced its cultural renaissance during the Bhakti Movement. This movement, spanning from the 7th to 17th centuries, emphasized personal devotion to a deity and brought forth an era of devotional poetry and songs that celebrated personal and often romantic expressions of love.
Poets like Mirabai and Kabir articulated themes of divine love that also echoed human romantic sentiments. This period laid the groundwork for a more emotional and individualized approach to relationships, albeit still within a framework of devotion and duty.
The 19th and Early 20th Centuries: Love as a Foundation
In the 19th century, the concept of marrying for love started to become widely embraced, especially in Western cultures. In India, under British colonial influence, the idea of marrying for love began to receive some recognition, particularly among the educated upper class. The advent of Western education and literature introduced new ideas about romance and individual choice. The Romantic Movement further emphasized individual feelings and emotional connections. Novels like Jane Austen’s "Pride and Prejudice" highlighted the importance of love and mutual respect in marriage.
The early 20th century saw the rise of companionate marriage, where partnerships were based on mutual affection, companionship, and shared interests. The growing influence of psychoanalysis and the study of human behavior also began to shape modern ideas about intimacy and romantic connections.
Contemporary Times: Diversity and Freedom
In the 21st century, romantic relationships are more diverse and flexible than ever before. The traditional model of heterosexual monogamous marriage arranged marriages in the case of India, is now one of many forms of romantic partnerships. Societal acceptance of various relationship structures has broadened significantly, influenced by changing norms, greater advocacy for individual rights, and the impact of globalization and technology.
Now let's come to the ‘today's romantic relationships’ we were discussing about. The evolution of times led us to today's era where no more ‘duties over desire’ kind of ideas are fed, these romantic relationships are needs of humans more than wants. Amongst all, these relationships are majorly driven by emotions. The fuel driving these relationships is inconsistent so is this arrangement. Thus it leads to different types of this romantic kinship. The types of romantic kinship not only vary from each other but their status may be measured as good or bad on many bases, including social, ethical, practical, and illegal.
And this has been the status forever. Most of the time, these relationships weren’t simply between one man loving one woman, neither then nor now. Let's discuss the types… we will try to cover as many aspects of this as possible.
Types and Definitions of Relationships Today:
Monogamous Relationships: Traditionally the most common form, involving exclusive romantic and sexual partnership between two people.
Open Relationships: Partners agree to engage in romantic or sexual activities with others outside the primary relationship.
Polyamorous Relationships: Multiple consensual romantic relationships exist simultaneously, with an emphasis on openness and communication.
Casual Dating: Non-committed relationships where individuals date and engage in romantic activities without the expectation of long-term commitment.
Long-Distance Relationships: Romantic partnerships where partners live apart geographically, maintaining the relationship through digital communication and occasional visits.
Non-Binary and LGBTQ+ Relationships: Reflecting a broader understanding of gender and sexuality, these relationships challenge traditional norms and celebrate diverse identities.
Friends with Benefits: Relationships where individuals maintain a friendship that includes sexual intimacy without romantic commitment.
Ideologies Then and Now
Then:
Duty and Obligation: Relationships were primarily about fulfilling societal roles and obligations.
Economic and Political Alliances: Marriages served as tools for economic gain and political alliances.
Patriarchy: Men held dominant roles, with women's roles often limited to domestic spheres and childbearing.
Now:
Individual Choice: Emphasis on personal happiness, emotional connection, and mutual respect.
Equality and Partnership: More egalitarian relationships with shared responsibilities and decision-making.
Diversity and Inclusion: Acceptance of diverse sexual orientations, gender identities, and relationship structures.
The journey from duty-bound unions to love-based partnerships and the acceptance of diverse relationship forms illustrates how romantic relationships have evolved to reflect broader changes in societal values and individual freedoms. Today, the rich tapestry of romantic connections celebrates the complexity and uniqueness of human relationships, offering more room for personal expression and fulfillment than ever before. This is the first article of the series where we will discuss these types and will try to understand better, the essence of romanticism in times where we live.
Check out Hello Fitness Magazine. There is never a wrong time to go on a fitness quest. Contact us and allow us to assist you in leading a better lifestyle. Follow us on Instagram. We share the best Health & Fitness related Articles for information based on healthy eating, health and fitness recommendations, health problems and their solutions, human body fitness, and much more.